24
2024
-
01
Clever trick to uncover, removal method of total nitrogen in wastewater
Author:
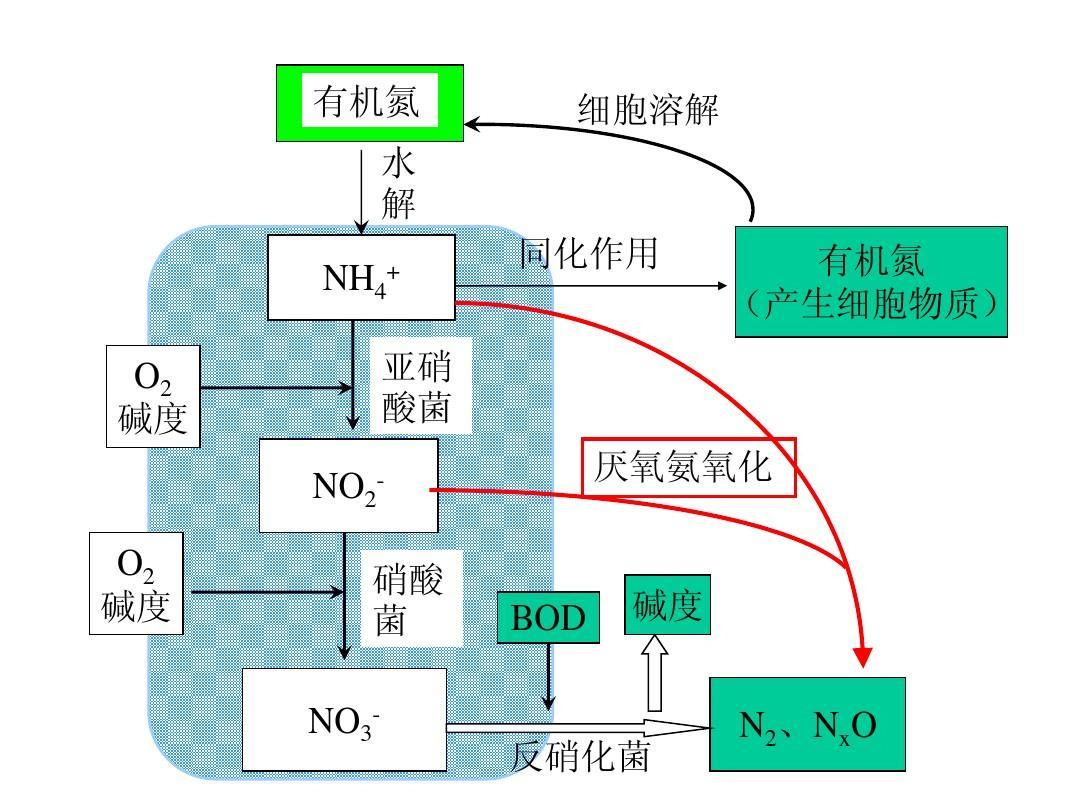
TN
TN needs to look at the hypoxic stage. First, clarify the main conditions for denitrification:
1. Carbon source;
2. Dissolved oxygen;
3. Reflux ratio;
4. The degree of ammonia nitrogen oxidation.
01
carbon source
If TN also has a specific drug, then the carbon source must be a specific drug for removing total nitrogen.
As is well known, denitrification reactions mainly occur in the anoxic stage; Under anaerobic conditions, denitrifying bacteria will use organic carbon sources as electron donors and nitrate nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen as electron acceptors for denitrification reactions. When there is an appropriate amount of carbon source in the anoxic tank, denitrifying bacteria receive good nutrient supplementation, and a large number of microorganisms proliferate, leading to denitrification reactions and a decrease in TN.
However, there have also been cases where TN suddenly increased and a large amount of carbon sources were added, but TN was not controlled and instead the COD in the effluent exceeded the standard. Have you ever encountered any water enthusiasts and how do you solve them?
There are many types of carbon sources that denitrification can utilize. Currently, commonly used ones include glucose, methanol, acetic acid, sodium acetate, new carbon sources, etc. With so many types of carbon sources, do you know which type of wastewater is suitable for which carbon source? Another economic issue is how to invest the least amount of carbon sources while ensuring compliance?
02
dissolved oxygen
As mentioned earlier, denitrifying bacteria belong to facultative anaerobic bacteria. In the case of high dissolved oxygen, oxygen will be prioritized for aerobic reactions, and the carbon source will be wasted. Therefore, the dissolved oxygen in the anaerobic zone should be reduced as much as possible, preferably controlled below 0.2mg/L
03
Reflux ratio
Everyone knows that internal and external reflux; The purpose of internal reflux is to reflux the nitrate nitrogen generated in the aerobic section to the anoxic zone, while the purpose of external reflux is to supplement sludge to the biochemical system and also to supplement nitrate nitrogen.
In a denitrification system, if TN removal is not considered without assimilation, the TN removal rate can be simply calculated using the ratio of internal and external reflux. The formula is as follows: theoretical removal rate=(R+r)/(1+R+r).
Whether the removal rate is 60%, 70%, 80%, or more or less. How to use our own system to improve efficiency as much as possible under limited conditions? Should we turn on internal reflux and control the proportion of internal reflux? Do you know this?
04
Ammonia nitrogen oxidation
Ammonia nitrogen oxidation requires a certain alkalinity, and anaerobic effluent must ensure an appropriate pH value. The COD should be low and the mud age should be long, otherwise the ammonia nitrogen oxidation effect will be poor; The effect of ammonia nitrogen is poor, and the reflux liquid is useless when it flows back to the anoxic zone, ultimately resulting in high ammonia nitrogen in the effluent.
COD
The COD of the system exists in three forms in wastewater, namely dissolved, colloidal, and suspended. These three different forms are removed in different ways in the system.
The removal of COD is relatively easier to calculate. It mainly depends on factors such as influent concentration, sludge volume, dissolved oxygen in the aerobic section, and inhibition conditions. There are also corresponding formulas.
However, the sudden increase in COD and BOD in the effluent of the secondary sedimentation tank reflects the malfunction of sewage treatment, which can be caused by external or internal factors leading to functional failure. It is necessary to classify harmful substances properly. To identify its characteristics, the first step is to determine the effluent COD; Analyze the phenomenon of increased COD and BOD5 values in wastewater treatment, most of which are caused by granular substances or soluble compounds, and there are multiple methods to determine the causes of their occurrence.
Related Products
Biological nitrogen removal process of low temperature wastewater
2024-05-28
Prevention and treatment of calcium carbonate scaling in reverse osmosis operation
2024-05-22
Treatment of pyrazolone production wastewater - bipolar membrane electrodialysis process
2024-05-20
How much salt does sewage contain that can enter the biochemical system?
2024-05-17
Huanke Environmental Protection Technology
HOTLINE:
Address:Gongye 1st Street, Weicheng District, Weifang City, Shandong Province China
Contact:Zhang Gong
Phone:+86-18865361829
Email:sdhuanke@163.com


Consult
Copyright © 2023 Shandong Huanke Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd