08
2024
-
01
Summary of AO process operation control indicators
Author:
The operation of sewage treatment requires the reasonable regulation of numerous control parameters, only in this way can the normal and efficient operation of the treatment process be guaranteed. This article provides a detailed introduction to the control of the main parameter indicators of AO (denitrification) process.
1. PH value
The pH range that a general sewage treatment system can withstand is 6-9, and if it exceeds this range, chemical blending agents need to be added for adjustment;
A too low pH value can cause small coagulation flocs and reduced activity of protozoa in biological treatment; If it is too large, it manifests as coarse coagulation flocs, turbid effluent, disintegration of activated sludge, and death of protozoa.
2. B/C
For activated sludge systems, it is generally believed that B/C ≥ 0.3 indicates good biodegradability and effective biological treatment.
When the biodegradability is less than 0.3, the organic matter content in the wastewater is insufficient to meet the needs of microbial growth in biological treatment, resulting in low efficiency of biological treatment. In this case, the control method is to add organic nutrients to the wastewater.
3. Hydraulic retention time (HRT)
For biological treatment, HRT must meet the corresponding process requirements, otherwise the hydraulic retention time is insufficient, the biochemical reaction is incomplete, and the treatment degree is weak; Excessive hydraulic retention time can lead to sludge aging in the system.
When the treatment effect is poor, the HRT can be checked according to the design value. If the HRT is too small, the sewage volume should be slowly reduced, and if it is too large, the sewage volume should be slowly increased.
4. Sludge concentration MLSS and MLVSS
MLSS is mainly calculated based on the food to food ratio, generally controlled between 2000-4000mg/L. If the proportion of MLVSS to MLSS is less than 55%, it indicates that ① there are too many inorganic substances, and the sand settling system should be checked; ② Insufficient organic nutrient sources in sewage, calculated using B/C and food microbiology ratios.
5. Sludge settling ratio SV30
The SV30 for stable processes ranges from 15% to 35%. If the inorganic content in the sludge is relatively high, it may be due to excessive sludge activity or sludge bulking.
6. Sludge Index (SVI)
The traditional activated sludge method has a normal value of 70-150. SVI mainly reflects the degree of looseness of sludge. When MLSS is very high, it is not accurate to use SV alone to judge sludge settling, and SVI must be combined. The regulation of SVI is mainly achieved through the adjustment of MLSS.
7. Food micro ratio F/M
The F/M range of AO denitrification process is between 0.1 and 0.15, and the food to microbial ratio exceeds the guidance range. If it is too low, it often leads to poor sludge activity and reduces the removal rate of pollutants.
If the food to biomass ratio is too high, excessive carbon sources cannot be metabolized into the aeration tank, which can lead to abnormal nitrification reactions and, in severe cases, collapse.
8. Mud age SRT
The sludge age of AO denitrification process is generally controlled at around 15-20 days, which is only a reference value. Each factory also needs to confirm the appropriate sludge age based on their own situation and seasonal changes.
If the sludge age is too short, the nitrifying microorganisms will be discharged from the system without enough time to reproduce, which cannot form dominant microorganisms and is not conducive to the degradation of ammonia nitrogen; However, if the sludge age is too long, the sludge will age, causing the secondary sedimentation tank sludge to float and the effluent to be turbid.
9. Aerobic tank DO
In aerobic area, the dissolved oxygen content of 2-4mg/L can meet the requirements of facultative or aerobic microbial activities. Generally, the sewage oxygenation capacity in winter is greater than that in summer, and the dissolved oxygen solution is higher in rainstorm period. Hypoxic zone, with a dissolved oxygen content of 0-0.5mg/L, meeting the requirements for denitrification bacterial reaction.
10. Oxygen deficient pool ORP
Different microorganisms require different redox potentials. Generally, aerobic microorganisms can grow above+100mV, with the most suitable range being+300mV to+400mV; Facultative anaerobic microorganisms undergo aerobic respiration above+100mV and anaerobic respiration below+100mV;
The requirement for specific anaerobic bacteria is -200mV~-250mV, among which the requirement for specific anaerobic methanogenic bacteria is -300-400mV, and the most suitable is -330mV.
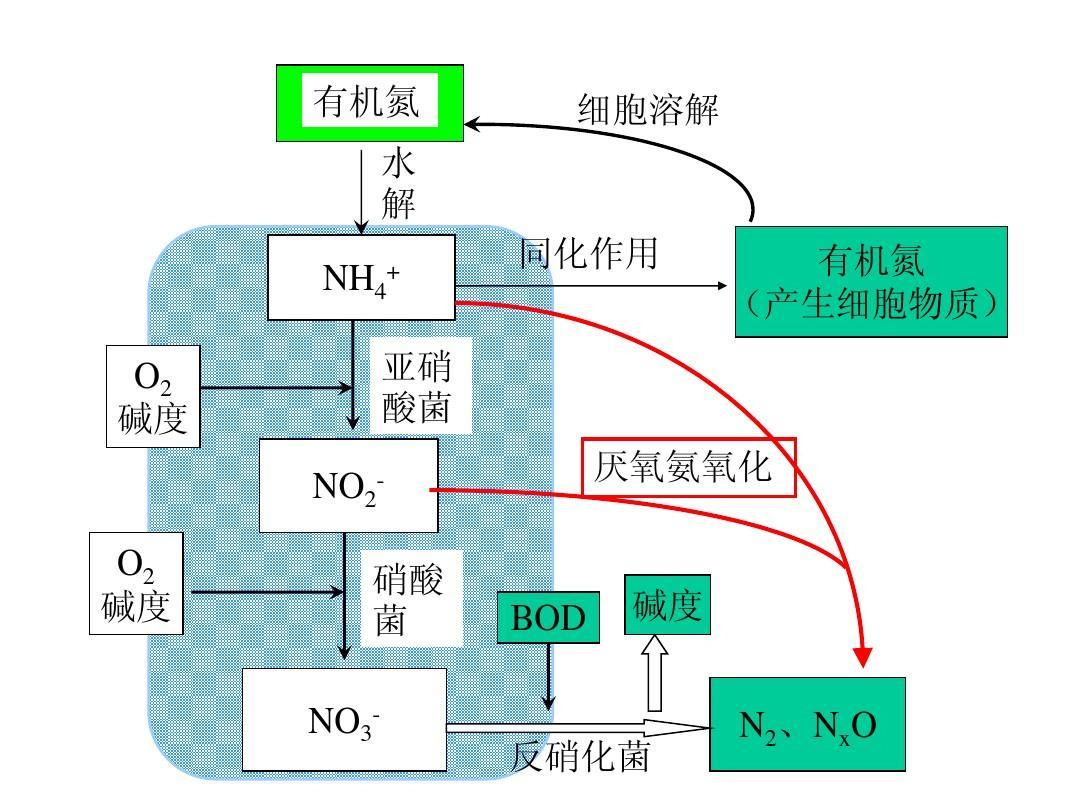
11. CN ratio
In theory, a ratio of 2.86 between influent COD and TN can meet the denitrification requirements. However, in practical operation, due to the influence of DO and other factors, the CN ratio is generally between 4-6 to meet the denitrification requirements.
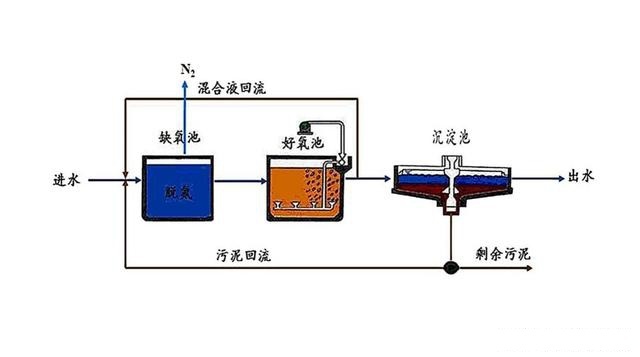
12. Reflux ratio
The reflux ratio of AO denitrification process is divided into internal reflux ratio and external reflux ratio. The external reflux ratio is generally controlled within the range of 30% -100%. The internal reflux ratio is generally controlled between 200% and 400%.
Related Products
Biological nitrogen removal process of low temperature wastewater
2024-05-28
Prevention and treatment of calcium carbonate scaling in reverse osmosis operation
2024-05-22
Treatment of pyrazolone production wastewater - bipolar membrane electrodialysis process
2024-05-20
How much salt does sewage contain that can enter the biochemical system?
2024-05-17
Huanke Environmental Protection Technology
HOTLINE:
Address:Gongye 1st Street, Weicheng District, Weifang City, Shandong Province China
Contact:Zhang Gong
Phone:+86-18865361829
Email:sdhuanke@163.com


Consult
Copyright © 2023 Shandong Huanke Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd