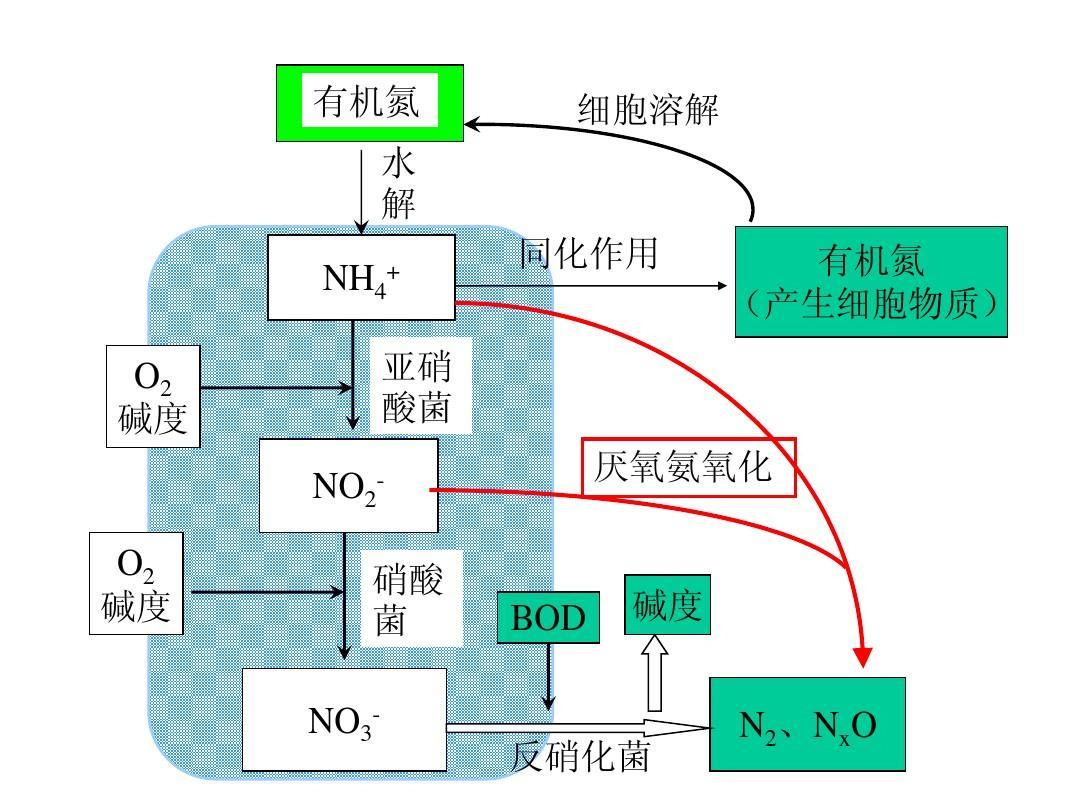
18
2023
-
12
Several summaries of biochemical treatment technology
Author:

The advantages and disadvantages of activated sludge method and biofilm method. Like biofilm method, activated sludge method belongs to aerobic biological treatment method. However, the activated sludge method relies on the suspended and flowing activated sludge in the aeration tank to decompose organic matter, while the biofilm method relies on the microbial membrane fixed on the surface of the carrier to purify organic matter. Taking the activated sludge method as a reference, compare their advantages and disadvantages:
1. Advantages of biofilm method: The biofilm fixed on the solid surface has strong adaptability to changes in wastewater quality and quantity, and good operational stability. No sludge bulking occurs, making operation and management more convenient. The activated sludge method is prone to sludge bulking. Due to the fixation of microorganisms on solid surfaces, even slow-moving microorganisms can grow and reproduce. In the activated sludge process, microorganisms with longer generation periods than residence times are discharged from the aeration tank, resulting in a more abundant biofilm and a certain distribution of biological populations along the water flow direction. The presence of microorganisms with high nutritional levels results in a greater transfer of organic matter metabolism into energy, resulting in a lower amount of residual sludge for the synthesis of new cells. Adopting natural ventilation for oxygen supply.
2. Disadvantages of biofilm method: Active organisms are difficult to manually control, resulting in poor flexibility in operation. The activated sludge method is more convenient and flexible to operate. Due to the small specific surface area of the carrier material, the equipment has limited volumetric load and low spatial efficiency. And it requires a lot of carrier fillers and support structures, usually with infrastructure investment exceeding that of activated sludge method. The treated effluent often contains a large amount of detached biofilm, which reduces the clarity of the resulting water. The activated sludge method obtains relatively good clarified water under normal conditions.
Advantages and disadvantages of aerobic and anaerobic methods, usage conditions
Compared with aerobic biological treatment, anaerobic biological treatment has the following advantages: no need for oxygenation, greatly reduced operating energy consumption, and the ability to convert organic pollutants into biogas for utilization. The amount of sludge produced is very small, and the cost of remaining sludge treatment is low. The yield of acid producing bacteria sludge is 0.15-0.34kg (VSS)/[kg (COD)], the yield of methane producing bacteria sludge is about 0.03kg (VSS)/[kg (COD)], and the yield of aerobic microbial sludge can reach 0.25-0.6kg (VSS)/[kg (COD)]. Suitable for treating refractory organic wastewater or as a pre-treatment process for highly refractory organic wastewater to improve its biodegradability and subsequent aerobic treatment efficiency. The combination of anaerobic and aerobic processes can play a role in nitrogen and phosphorus removal. The demand for nutrients is small. It is generally believed that the demand for nitrogen and phosphorus in aerobic treatment is BOD: N: P=100:5:1, while in anaerobic treatment it is (350-500): 5:1. Organic wastewater generally contains a certain amount of nitrogen, phosphorus, and various trace elements, so anaerobic treatment can add no or less nutrients. Strong resistance to impact loads. Anaerobic treatment of sludge has a high concentration and can withstand significant changes in concentration and water quality. Flexible scale. The anaerobic treatment system is flexible in scale, can be large or small, has simple equipment, and is easy to manufacture.
2. Compared with aerobic biological treatment, anaerobic biological treatment has the following disadvantages: although the anaerobic method has high load, absolute removal of organic matter, and high inlet concentration, its effluent COD is higher than aerobic treatment, and in principle, post-treatment is still needed to achieve higher drainage standards. Anaerobic microorganisms are more sensitive to toxic substances, therefore, insufficient understanding of the properties of toxic wastewater or improper operation may lead to deterioration of reactor operating conditions in severe cases. The initial start-up process of anaerobic reactors is slow and generally takes 8-12 weeks. A2/O synchronous denitrification and phosphorus removal process flow, and briefly describe the role of each part in anaerobic reactors: phosphorus removal bacteria complete the release of phosphorus and uptake of organic matter here. Hypoxic reactor: The main function of this section is denitrification. Nitrate nitrogen is sent from the aerobic tank through internal circulation, and the mixed liquid in the circulation is relatively large, usually twice the inflow rate. Aerobic reactor: The mixed liquid enters the aerobic reactor aeration tank from the anoxic reactor. This reactor is multifunctional, and reactions such as BOD removal, nitrification, and phosphorus absorption are all carried out here in the sedimentation tank. Mud water separation is carried out, and the supernatant is discharged as treated water. Part of the settled sludge flows back to the anaerobic tank, while the other part is discharged as residual sludge.
Advantages and disadvantages of A2/O:
Advantages: Simple process and short total stay time; Anaerobic (anoxic) aerobic alternation operation is not suitable for the proliferation and reproduction of filamentous bacteria, and the possibility of sludge bulking is extremely low; No need for medication or additional carbon sources, low operating costs;
Disadvantage: The retention time of sludge in the sedimentation tank should not be too short; The denitrification and phosphorus removal effect is not very good.
Discuss the process and characteristics of using A/O technology for denitrification and phosphorus removal, where sewage and reflux sludge enter the first anoxic tank (A) of the system simultaneously. At the same time, a portion of the fully reacted digestive liquid in the subsequent reactors also flows back to the anoxic tank (called digestive liquid reflux or internal circulation). The denitrifying bacteria in the anoxic tank use organic matter in wastewater as electron donors and nitrate (or nitrite) in the reflux solution as electron carriers for anaerobic respiration, reducing nitrate nitrogen in the reflux solution to nitrogen and releasing it to complete the denitrification process; Afterwards, the mixed liquid enters the aerobic tank, where nitrifying bacteria oxidize the ammonia nitrogen in the wastewater into nitrate nitrogen, which then flows back into the anoxic tank to make necessary preparations for denitrification. The anaerobic pool and aerobic pool have complementary and mixed microorganisms, each always in the best ecological environment.
Advantages: The process is simple and does not require additional carbon sources, resulting in lower infrastructure and operating costs.
Disadvantage: The effluent contains a certain concentration of nitrate, which may cause denitrification reaction in the sedimentation tank, causing sludge to float and affecting the effluent quality. Wastewater and phosphorus containing reflux sludge (containing polyphosphate accumulating bacteria) enter the anaerobic tank synchronously. Under adverse anaerobic conditions, polyphosphate accumulating bacteria decompose and release phosphorus accumulated in the bacterial body, and uptake organic matter. Then, the sewage mixture enters the aeration tank. Under aerobic conditions, the phosphorus accumulating bacteria can absorb excessive phosphorus, and most of the organic matter in the sewage is also oxidized and degraded in the tank. The removal rate of BOD5 is roughly the same as that of a typical activated sludge system, with a higher removal rate of phosphorus.
Advantages: The process flow is simple, without the need for medication or internal circulation, resulting in lower infrastructure and operating costs. Moreover, due to the absence of internal circulation, the anaerobic tank can maintain a good anaerobic state.
Disadvantages: The phosphorus removal rate of this process is difficult to further improve, and it is also prone to phosphorus release in the sedimentation tank.
Related Products
Biological nitrogen removal process of low temperature wastewater
2024-05-28
Prevention and treatment of calcium carbonate scaling in reverse osmosis operation
2024-05-22
Treatment of pyrazolone production wastewater - bipolar membrane electrodialysis process
2024-05-20
How much salt does sewage contain that can enter the biochemical system?
2024-05-17
Huanke Environmental Protection Technology
HOTLINE:
Address:Gongye 1st Street, Weicheng District, Weifang City, Shandong Province China
Contact:Zhang Gong
Phone:+86-18865361829
Email:sdhuanke@163.com


Consult
Copyright © 2023 Shandong Huanke Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd